Globalization, Connectivity, Digitization and Global Economic Reforms have brought about unprecedented changes to the world. The continuous shifts in digital technology have changed the way individuals, groups and organizations behave and interact with one another. The power of technology led the shift towards increased adaptability and affordability of mobile phones as a means to connect world-wide. Moreover, the upsurge of internet services like 3G, 4G, LTE and now 5G have increased customer engagement.
One of the many effects of globalization on developing nations is the rise of cash payments in traditionally barter economies.
Almost 2 billion people from poverty struck areas, forming 40% of the world’s adult population have a mobile phone but lack one of the very basic necessities of life: a bank account. Click To Tweet
This is largely because either the people don’t have enough resources to open and maintain bank accounts or the banks don’t get the required minimum return on investment by operating in such locations or targeting such groups of people, hence limit their services to wealthy or affording groups only.
This means not enough provisions and instruments have been provided to individuals falling on or below the poverty line in order for them to improve their lifestyle. These people struggle to live, earn money and feed their families. Exclusion from the formal financial system and the growing gap between banked and unbanked individuals is a hindrance in the prosperity of middle-class life which needs to be reduced to increase inclusion in our societies. This gap could exist for multiple reasons including:
- Inconvenience in rely on the banking network
- Stringent bank account opening requirements
- Not enough money to open and maintain accounts
- No need for bank accounts or banking facilities
Financial inclusion is one of the key drivers and a critical enabler for poverty reduction and inclusive growth.
Access to financial services ensures that households and businesses regardless, of their income levels can use these services to improve the quality of their lives.
Extending innovative models to give access to financial services to the poor has now become an urgent challenge. This has been dealt with by the modern technologies that have merged two sectors: telecommunications and banks. The mobile financial services have added value to the individuals’ lives and more importantly have overcome barriers to financial inclusion that were otherwise increasingly constantly. The most important factor in play here was the increased mobile penetration in developed countries has led to an increase in the mobile money market.
Mobile Money
Mobile money, also commonly known as mobile payment, mobile money transfers and mobile wallet, refers to the money held in electronic accounts (wallets), which are associated with the unique mobile number of a telecom subscriber. Since the reach of telecom operators is much larger (and constantly increasing) than that of the formal banking sector, mobile money certainly offers the prospect of a low-cost solution to create access to the financial sector.
Seamless Distribution Systems (SDS) transforms the mobile phone into a digital payment and money transfer tool, enabling easy access to mobile financial services for those who have limited resources or restricted access to traditional banking and financial services. This solution, powered by our transaction platform ERS 360°, provides a convenient means to conduct financial transactions without the worry of the type of mobile device or level of financial or technical knowledge of the user. ERS 360° is the brand name of Seamless’ Electronic Transaction platform that provides mobile operators and distributors around the world with a complete range of solutions, including Mobile Financial Services as well.
Seamless Mobile Money is a pre-funded service, which means that all the electronic money that it handles must exist as funds against physical money in a settlement account at a partner bank, before the equivalent electronic money can be transferred within the system. It requires the mobile subscriber and the merchants (agents who transfer credit to the subscribers) to have mobile money (MoMo) accounts directly linked with an account at the partner bank. The MoMo account stores virtual money for the subscriber and enables them to carry out transactions. Two types of accounts exist to make the transaction flow easier and easily distinct:
- Mobile Money Account in the Telecom Domain
- Mobile Money Account in the Financial Domain
Seamless Mobile Processing solution processes transactions by gathering relevant parameters as input and performing the validation and authorization.
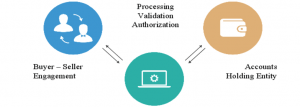
Process validation
Mobile money is a way for the Service Provider to expand its customer base, reduce churn rate, improve reseller and customer loyalty, generate increased sales and new transaction flow to optimize the utilization of resources.
Using our services, the Service Provider is able to provide a wide range of offerings to the end user which provide a safe and secure alternative to cash payments. SDS enables the Service Providers to extend Mobile Wallets to the subscribers.
Mobile Wallet or Mollet, as we call it, is a highly secured digitally stored value account that allows the users to store, send and receive money directly from their mobile phones, without the need to carry cash or cards. SDS gives complete freedom to Service Providers to customize the digital wallet according to specific business needs. The subscriber is simply to register his account with the Service Provider and integrate it with his/her bank account. Integrating the MoMo account with the bank account allows the users to have 24/7 access to money. It facilitates the easy flow of money between different channels making the transaction ecosystem more accessible and convenient for the subscriber. Using Mollet, the subscriber can use two services:
- Cash-in: Cash in is a service, which enables a user to load his/her mobile money account, and is done through authorized mobile money agents.
- Cash-out: Cash-out is a service, which enables a user to unload funds from his/her mobile money account, and is done through authorized mobile money agents.
Mobile money offerings are not just limited to a subscriber holding an account, but comes equipped with a Payment and Commerce solution. This allows the users to pay their bills as well as make payments to merchandisers anywhere anytime through their stored value accounts.
Additionally, it allows Peer-to-peer transfer. This means the subscribers are able to carry out monetary transfers between two account holders, be it Agent-to-Agent, User-to-User or Agent-to-User. P2P transfer follows strict compliance rules by carrying out a comprehensive KYC ensuring user traceability and transparency of all transactions.
Extending Mobile Financial Services to users not only reduces the ratio of the unbanked population but also enables the isolated citizens to become part of and engage in commercial activities. Click To Tweet
SDS ensures that part of this engagement is also extended towards including the the banked population in terms of money transfers over long distances. Before mobile money the costs involved in long distance transactions were very high. Therefore, users could not easily form financial sharing links with relatives, friends in distant areas. Mobile money makes it possible for the users to send money domestically or internationally. It enables a quick, cheap and secure alternative for users to perform transactions paving way for a wider network of social support.
While the Mobile Financial Services are able to provide a way for the unbanked to hold an account and carry out transactions, for the Service Provider it means an increased number of mobile users, consequently resulting in increased revenues.


