The telecommunications industry continues to undergo substantial changes due to technological advances. As the end of the decade approaches, 2020 has already presented new challenges as well as vast opportunities for the industry.
Growth of the telecommunications industry
According to a GSMA report, in 2020, the global telecom market has reached approximately 5.6 billion unique subscribers and 5.8 billion smartphones. Operator revenues have increased to $1.2 trillion from $1.1 trillion in 2015. Forecasts predict a higher number of mobile network connections and increased smartphone adoption in the future, but there is more to these numbers than that. These projections require telecom operators to plan and expand their operations and make infrastructural changes to solve challenges that come with technological advancements.


Source: GSMA
Challenges facing the telecommunications industry
One of the biggest challenges facing the telecommunications industry nowadays is the rising need for capital expenditure (CAPEX). In an EY report (2019), telecom operators were asked to rank prominent issues relating to their business operations. The majority pointed towards the growing CAPEX requirement as the main issue followed by the need to improve margins and meet strict regulatory requirements.
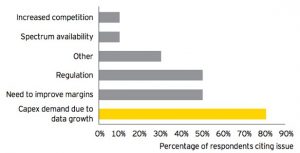
Source: EY
Growing demand for mobile data services
As mobile internet penetration increases globally, voice and SMS services are being replaced by mobile applications that use data rather than cellular networks. For example, WhatsApp, an instant messaging service, is used to send messages using mobile data instead of standard SMS services. As mobile internet coverage becomes more widely available and accessible, this trend is expected to persist, with data traffic and bandwidth requirements growing worldwide.
Operators will need to invest in infrastructure
Growing demand will put pressure on operators to invest more in scalable infrastructure and internet facilities that can support increased traffic and provide high-quality data services to customers. In addition, operators can introduce data bundle packages for video streaming, social media, or messaging services to encourage data usage to compensate for the dwindling revenue from voice and SMS services. For example, South African multinational, MTN, introduced data bundles that allow subscribers to purchase customized data packs at a low price.
Mobile operators not only have to find ways to raise additional revenues, but they also must take measures to reduce costs, increase sustainability, and optimize business operations. Using managed services is another option that can help operators achieve cost efficiencies and improve the quality of the services provided to mobile subscribers. They can outsource operations of some of their business units like sales, customer service, and billing or they can rely on another company for their entire hardware and infrastructure needs.
Read more on end-to-end system maintenance, monitoring, and management services.
Likewise, another challenge that telecommunication companies will have to face in the future is the saturation of mobile penetration levels in developed markets. Operators will need to switch their focus from developed markets to emerging economies where there are greater opportunities for expansion of mobile network connections.
However, to benefit from this situation, telcos need to leverage innovative digitization strategies and focus on ways to promote financial inclusion. These types of projects not only lead to an increase in mobile network connections, but they can also contribute towards longer-term economic and social development in emerging markets.
The Internet of Things presents new opportunities
Lastly, the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) presents challenges as well as opportunities for mobile operators. For consumers to become a part of an environment where devices and humans are interconnected, they depend on telecommunication companies to provide them with reliable and high-speed internet connections.
Telcos can capitalize on this dependency by collaborating with companies driving the IoT phenomenon. For example, AT&T has partnered with companies like Cisco, Ericsson, GE, IBM, Intel, and Deloitte for its “Smart Cities” initiative. The aim of this initiative is to enable city officials to monitor different aspects related to infrastructure, public safety, and transportation remotely from their devices and take action in real-time.
With these challenges facing the industry, telecom operators will need to adapt and reinvent themselves in order to remain competitive. Forming partnerships through mergers and acquisitions, rolling out projects that provide high-speed network access, adopting cost-efficient strategies like outsourcing managed operations, and making smart investment decisions in advanced infrastructure and technology will be key to providing exceptional service and meeting customer expectations.



